Kicking off with Fixed-rate bonds vs floating-rate bonds, this comparison delves into the intricacies of both types of bonds, shedding light on their differences and advantages.
Exploring the nuances of fixed-rate and floating-rate bonds, this discussion aims to provide clarity for investors looking to make informed decisions.
Fixed-rate bonds

Fixed-rate bonds are a type of bond where the interest rate remains constant throughout the life of the bond. Investors who purchase fixed-rate bonds receive a predetermined interest payment at regular intervals until the bond reaches maturity.
Comparison with other types of bonds
When compared to other types of bonds, such as floating-rate bonds or inflation-linked bonds, fixed-rate bonds provide investors with a predictable income stream. This predictability can be attractive to risk-averse investors looking for stable returns.
Advantages of investing in fixed-rate bonds, Fixed-rate bonds vs floating-rate bonds
- Stability: Fixed-rate bonds offer a stable and predictable income stream, making them a reliable option for investors seeking regular interest payments.
- Interest rate risk protection: Since the interest rate is fixed, investors are shielded from fluctuations in the market that could affect the value of their investment.
- Easy to understand: Fixed-rate bonds are straightforward investments, making them accessible to a wide range of investors, including those who may be new to the bond market.
Floating-rate bonds
_Article+graphic+05+(1).jpg?w=700)
Floating-rate bonds are debt securities with variable interest rates that are adjusted periodically based on a reference rate, such as LIBOR or the Treasury bill rate, plus a predetermined spread. Unlike fixed-rate bonds, the interest payments on floating-rate bonds fluctuate in response to changes in market interest rates.
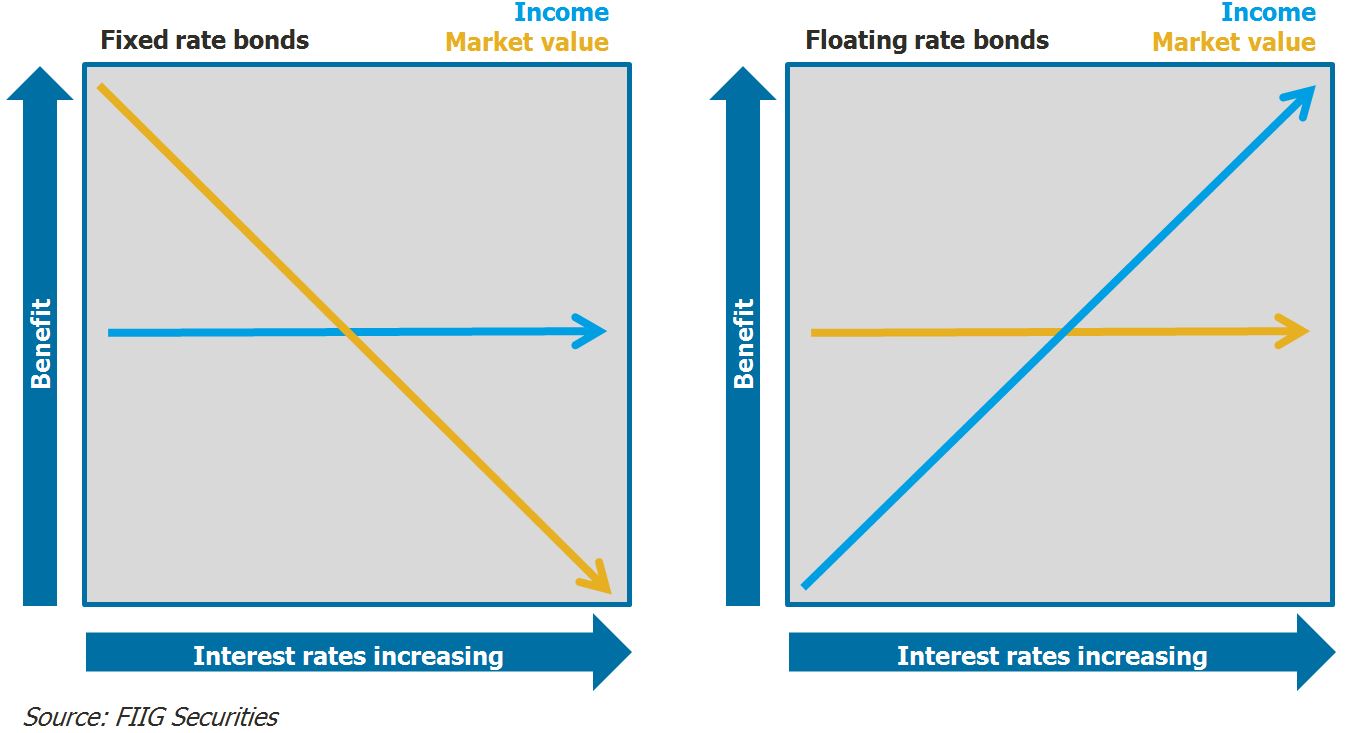
Investors might choose floating-rate bonds over fixed-rate bonds in a rising interest rate environment. When interest rates are expected to increase, the interest payments on floating-rate bonds also rise, providing investors with a way to potentially benefit from higher rates. Additionally, floating-rate bonds are less sensitive to interest rate risk compared to fixed-rate bonds, making them attractive to investors seeking protection against interest rate fluctuations.
How interest rates affect floating-rate bonds
Interest rates have a different impact on floating-rate bonds compared to fixed-rate bonds. As market interest rates rise, the interest payments on floating-rate bonds increase, resulting in higher yields for investors. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the interest payments on floating-rate bonds decrease, potentially leading to lower returns for investors. This dynamic nature of floating-rate bonds makes them a flexible investment option that can adapt to changing market conditions.
Key differences: Fixed-rate Bonds Vs Floating-rate Bonds

Fixed-rate bonds and floating-rate bonds have distinct characteristics that set them apart in the bond market. Understanding the key differences between these two types of bonds is essential for investors looking to make informed decisions.
When it comes to fixed-rate bonds, the interest rate remains constant throughout the life of the bond. Investors receive a predictable stream of income over time, making fixed-rate bonds a popular choice for those seeking stability and certainty in their investments. On the other hand, floating-rate bonds have interest rates that fluctuate based on a benchmark or index. This means that the interest payments on floating-rate bonds can vary, providing investors with the opportunity to benefit from rising interest rates.
Impact of market conditions
Market conditions play a significant role in determining the performance of fixed-rate and floating-rate bonds. In a rising interest rate environment, fixed-rate bonds may underperform as their fixed interest payments become less attractive compared to newly issued bonds with higher rates. Conversely, floating-rate bonds tend to perform better in such conditions as their interest payments adjust upwards along with prevailing rates. On the other hand, in a declining interest rate environment, fixed-rate bonds may outperform floating-rate bonds as the fixed interest payments become more valuable.
Risks associated with investing
Investing in fixed-rate bonds carries interest rate risk, which refers to the potential for the value of the bond to decrease if interest rates rise. This risk is higher for fixed-rate bonds compared to floating-rate bonds, which have interest payments that adjust to prevailing rates. On the other hand, floating-rate bonds are exposed to credit risk, which is the risk of the bond issuer defaulting on payments. Investors in floating-rate bonds need to assess the creditworthiness of the issuer to mitigate this risk effectively.
Considerations for investors
When choosing between fixed-rate and floating-rate bonds, investors should consider various factors to make an informed decision. Economic indicators play a crucial role in influencing the performance of each type of bond. Additionally, different scenarios may arise where one type of bond may be more suitable than the other for an investor.
Interest Rate Environment
- Investors should assess the current interest rate environment before deciding between fixed-rate and floating-rate bonds. In a rising interest rate environment, floating-rate bonds may offer better protection against interest rate risk compared to fixed-rate bonds.
- Conversely, in a declining interest rate environment, fixed-rate bonds may be more favorable as they lock in a higher rate of return.
Credit Risk
- Consider the credit risk associated with each type of bond. Floating-rate bonds are typically less sensitive to changes in credit risk compared to fixed-rate bonds, as the interest payments adjust periodically based on a reference rate.
- Investors seeking higher credit quality may prefer fixed-rate bonds, as they offer a fixed interest rate throughout the bond’s term, providing more certainty in income payments.
Market Volatility
- Market volatility can impact the performance of both fixed-rate and floating-rate bonds. Investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer fixed-rate bonds, as they provide a steady stream of income regardless of market fluctuations.
- On the other hand, floating-rate bonds may be more suitable for investors willing to take on some level of interest rate and credit risk in exchange for potentially higher returns.
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between fixed-rate and floating-rate bonds is crucial for investors to navigate the complexities of the bond market effectively. By weighing the pros and cons of each type, individuals can make strategic investment choices tailored to their financial goals.
When looking for the best treasury bonds to buy, it’s essential to consider various factors such as the current market conditions and the bond’s maturity date. Researching and analyzing different options can help investors make informed decisions. For more information on the best treasury bonds to buy, check out this resource.
Investors seeking high-yield bonds for income should evaluate the risk associated with these investments. Understanding the potential returns and the issuer’s credit rating is crucial in making sound investment choices. To explore more about high-yield bonds for income, visit this source.
Staying informed about the bond market outlook is key for investors to navigate the fluctuations and trends in the market. Monitoring interest rates and economic indicators can provide valuable insights into the future performance of bonds. For the latest updates on the bond market outlook, refer to this site.