Understanding leverage in forex opens up a world of possibilities in trading, offering the potential for significant gains but also carrying inherent risks. Dive into this comprehensive guide to grasp the intricacies of leveraging your investments in the forex market.
Explore the different types of leverage, learn how to calculate leverage ratios, and discover effective strategies for managing leverage to optimize your trading experience.
Understanding Leverage in Forex
When it comes to forex trading, leverage plays a crucial role in amplifying both potential gains and losses. Understanding how leverage works is essential for traders to effectively manage their risk and maximize their profits in the forex market.
Definition of Leverage in Forex Trading
Leverage in forex trading refers to the ability to control a larger position size with a smaller amount of capital. It allows traders to open positions that are significantly larger than their initial investment by borrowing funds from their broker. For example, with a leverage ratio of 1:100, a trader can control a position worth $100,000 with only $1,000 in their trading account.
How Leverage Works in the Forex Market
Leverage works by using borrowed capital to increase the potential returns on an investment. While it can magnify profits, it also amplifies losses. Traders must be aware that trading with leverage involves a high level of risk and can lead to significant financial losses if not managed properly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Leverage in Forex Trading, Understanding leverage in forex
- Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, increasing the profit potential.
- It provides the opportunity to diversify trading strategies and take advantage of market opportunities that would otherwise be out of reach.
- However, using leverage also increases the risk of substantial losses, especially in volatile market conditions.
- Traders must exercise caution and implement risk management strategies to protect their capital when trading with leverage.
Examples of Leverage Amplifying Gains and Losses in Trading
For example, if a trader uses 1:50 leverage and the price of a currency pair moves in their favor by 2%, they would realize a 100% return on their initial investment. On the other hand, if the market moves against them by 2%, they would lose 100% of their capital.
Types of Leverage

When it comes to forex trading, there are different types of leverage that traders commonly use to amplify their positions. Each type of leverage has its own set of features and implications for trading strategies, as well as associated risk factors.
Understanding forex candlestick patterns is another key aspect of successful trading. These patterns can provide valuable insights into market movements and potential price reversals. Discover more about understanding forex candlestick patterns to enhance your trading strategy.
1. Standard Leverage
Standard leverage in forex trading typically refers to a leverage ratio of 1:100. This means that for every $1 in your trading account, you can control a position worth $100. While this type of leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses if the market moves against your position.
One of the essential skills in forex trading is knowing how to read forex price charts. By analyzing these charts effectively, you can identify trends and patterns to make profitable trades. Explore our guide on how to read forex price charts to improve your trading knowledge.
2. Mini Leverage
Mini leverage offers a lower leverage ratio compared to standard leverage, usually around 1:50. This type of leverage allows traders to control smaller positions with less capital, making it suitable for those who want to trade with lower risk exposure.
3. Micro Leverage
Micro leverage provides an even lower leverage ratio, typically around 1:10. This type of leverage is ideal for beginners or conservative traders who want to start with minimal risk. While the potential for profit is limited with micro leverage, it also helps in mitigating losses.
4. Variable Leverage
Variable leverage allows traders to adjust their leverage ratio based on market conditions or their risk tolerance. This type of leverage offers flexibility but requires careful monitoring and decision-making to optimize trading strategies effectively.
5. No Leverage (1:1)
Some brokers offer the option of trading without leverage, with a ratio of 1:1. While this eliminates the risk of amplifying losses, it also limits the potential for significant profits. Traders who prefer a conservative approach may opt for no leverage trading.
When starting out in forex trading, it’s crucial to understand the best forex indicators for beginners. These tools can help you make informed decisions and improve your trading strategy. You can learn more about the best forex indicators for beginners to enhance your trading skills.
Calculating Leverage Ratio

Calculating the leverage ratio in forex trading is crucial for understanding the amount of capital being used in relation to the size of the position. This ratio helps traders determine the level of risk they are taking on and the potential returns they could achieve. Here is a step-by-step guide on determining the leverage ratio for a trade and its significance in risk management.
Step-by-Step Guide on Determining Leverage Ratio
- Calculate the total value of the position: This includes the size of the trade and the current exchange rate.
- Determine the margin requirement: This is the amount of money required to open and maintain the position.
- Divide the total value of the position by the margin requirement to get the leverage ratio.
Leverage Ratio = Total Value of Position / Margin Requirement
Significance of Leverage Ratio in Risk Management
- Higher leverage ratios indicate a higher level of risk as a small price movement can result in significant gains or losses.
- Lower leverage ratios provide a cushion against market volatility and reduce the risk of margin calls.
- By understanding the leverage ratio, traders can adjust their position sizes to manage risk effectively.
Real-Life Scenarios
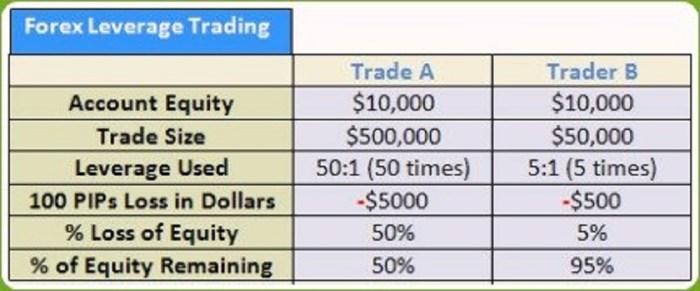
- Scenario 1: Trader A uses a leverage ratio of 1:100 on a $10,000 position. A 1% price movement could result in a $100 profit or loss.
- Scenario 2: Trader B uses a leverage ratio of 1:50 on a $5,000 position. A 2% price movement could lead to a $100 profit or loss.
Managing Leverage Effectively

Effective management of leverage is crucial in forex trading to ensure long-term success and minimize the risks associated with high leverage levels. By implementing appropriate strategies and risk management techniques, traders can navigate the volatile forex market more effectively.
Setting Appropriate Leverage Levels Based on Risk Tolerance
- Understand your risk tolerance: Before entering any trade, assess your risk tolerance level to determine the maximum leverage you are comfortable with.
- Avoid excessive leverage: Resist the temptation to use high leverage ratios, as they can amplify both profits and losses significantly.
- Consider your trading style: Scalpers may require higher leverage compared to swing traders, as their positions are held for shorter periods.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls Related to Excessive Leverage
- Use stop-loss orders: Set stop-loss orders to automatically close positions when a certain level of loss is reached, preventing further losses due to excessive leverage.
- Monitor your positions: Regularly review your open positions and adjust leverage levels if necessary to align with market conditions.
- Avoid emotional decision-making: Fear and greed can lead to impulsive trading decisions, including overleveraging. Stick to your trading plan to avoid such pitfalls.
Risk Management Techniques to Mitigate the Impact of Leverage
- Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across different currency pairs to reduce the impact of leverage on a single trade.
- Use proper position sizing: Calculate the appropriate position size based on your account size and risk tolerance to avoid overexposure to leverage.
- Implement a risk-reward ratio: Set clear risk-reward ratios for each trade to ensure that potential losses are limited relative to potential gains.
In conclusion, mastering the concept of leverage in forex is key to navigating the volatile landscape of currency trading. By understanding the nuances of leverage, traders can enhance their profitability while safeguarding against potential losses.